The 2PDF Command Line Syntax and Examples page shows the conversion settings that you can specify to adjust your file conversion with 2PDF. The command line syntax parameters determine how files are converted as well as the structure and features of resultant PDF documents.
- Quick start
- Command line structure
- Switches
- Common options (-options)
- PDF format parameters for converted files (-pdf)
- Operations (-oper)
- Page autorotation (-oper autorotate)
- Page cropping (-oper crop)
- 'Grayscale' operation (-oper grayscale)
- Page rotation (-oper rotate)
- Resizing (-oper resize)
- Rasterization (-oper rasterize)
- Text watermark (-oper textwatermark)
- Text annotation (-oper textannotation)
- Image watermark (-oper watermark)
- Draw rectangle (-oper paint)
- Remove blank pages (-oper removeblankpages)
- Post-processing actions (-postproc)
- File loading settings (-fls)
- Load custom 2PDF Settings (-inipath)
- Information (-info)
- Command lines (-cmdlines)
- Default settings (-ini)
- Examples
Quick start
- Press Win+R on your keyboard, type cmd and click OK to open the Command Prompt (CMD).
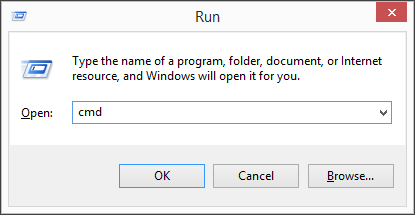
- To call 2PDF, type in 2PDF.exe and press Enter. You can get an entire list of available operations and options by using this command line:
2PDF.exe
- The command lines have arguments with values, which are typed after the command itself. In general, the basic syntax is as follows:
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out"
- -src should be followed by the source folder path with files to be converted or path to input file;
- Asterisk (star, *) is a wildcard character which stands for any string of characters (or no characters at all). *.* stands for any filename – point – any file extension;
- -dst should be followed by the destination folder path for output files;
- When specifying the source folder path (or source file) and destination path (output folder) – enclose them in double quotation marks. Example: -src "C:\Incoming files\For conversion\Invoice.docx".
- Press Enter to execute the command.
Command line structure
The basic command line structure sets the source for files and the destination path. After them you can add optional parameters for output PDF files such as file structure, handling attachments, page autorotation, and more.
2PDF command line structure looks like:
2PDF.exe -<switch1> [param1:value paramN:value] -<switchN> [parameters]
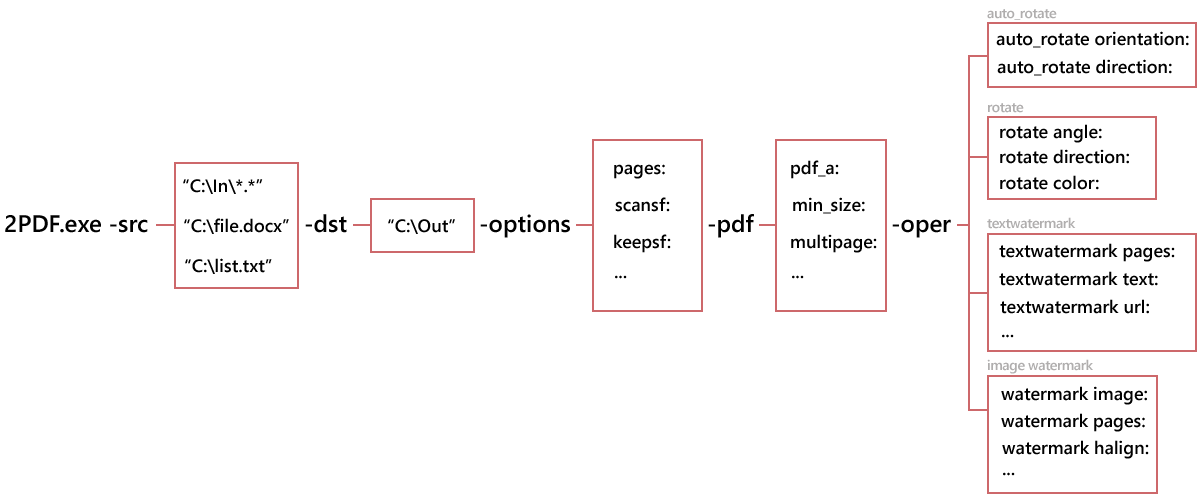
Switches
Use switches -src and -dst to set source for input files and output destination for converted files. You can also:
- Rotate document pages using -oper autorotate, -oper rotate switches;
- Add a watermark using -oper textwatermark or -oper watermark switches;
- Move, copy, or delete source files with -postproc switch;
- Set common parameters with -options and -pdf switches.
| Switch | Description | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -src | Sets a location of files that should be converted.
|
||||||||||||
| -dst | Sets the destination folder for the output PDF file(s). Example: -dst "C:\Output" | ||||||||||||
| -options | Sets up file processing and common 2PDF options. | ||||||||||||
| Sets PDF format options, such as multipage or OCR. | |||||||||||||
| -oper autorotate | Sets landscape or portrait orientation for output files. | ||||||||||||
| -oper crop | Performs page cropping. | ||||||||||||
| -oper grayscale | Makes output PDFs black-and-white (in shades of gray). | ||||||||||||
| -oper rotate | Rotates document pages at a specific angle. | ||||||||||||
| -oper resize | Changes the size of output images or document pages. | ||||||||||||
| -oper rasterize | Optimizes file size of a PDF by rasterizing its pages into JPEG format. | ||||||||||||
| -oper textwatermark | Adds a text watermark to document pages. | ||||||||||||
| -oper textannotation | Quickly adds text to document pages. | ||||||||||||
| -oper watermark | Adds an image watermark to document pages. | ||||||||||||
| -oper paint | Draws a rectangular border inside or around the output pages. | ||||||||||||
| -oper removeblankpages | Removes unnecessary blank pages automatically. | ||||||||||||
| -postproc | Performs additional post-processing actions: copy, move, or delete source or output files | ||||||||||||
| -fls | Defines file loading settings. | ||||||||||||
| -inipath | Set path and apply previously saved 2PDF Settings. | ||||||||||||
| -info | Displays file information, such as the page counter of a source file or bookmark list. | ||||||||||||
| -about | Shows license key and software version. Example: 2PDF.exe -about |
OR
| -cmdlines | Allows to run 2PDF command(s) from a TXT file. This can be helpful when the command is very long or if you want to run several commands sequentially. Example: 2PDF.exe -cmdlines "C:\Scripts\Command.txt" |
Common options (-options)
General file conversion options are controlled by the -options switch. Values that are marked bold below are set by default.
-options
| Parameter | Description | Value (values in bold are set by default) |
|---|---|---|
| pages: | Set page range. To select pages from the end of the document, use the expression "last" (last for the last page, last1 for the penultimate page, etc.). For example: 1,5,last2,last1,last |
all |
| scansf: | Convert files within subfolders too (if you specify a folder as a source) | yes, no |
| keepsf: | Keep the same subfolder structure as in the input folder (if you specify a folder as a source) | yes, no |
| mswildc: |
Enable/disable Microsoft DOS/Win32 wildcard matching algorithm. Learn more [+]
This algorithm is a bit different from the "expected" behavior, since some
wildcards work in a different way in Windows (compared to Linux, for example).
Suppose, you want to convert DOC files only. It would seem that you should just use this command: 2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.doc" But as a result, both .DOC and .DOCX files will be converted, which is not needed. To convert only files that match the specified file extension, disable the Microsoft wildcard matching algorithm. To do that, use the command: 2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.doc" -options mswildc:no |
yes, no |
| overwrite: | Overwrite existing files or skip them | no, yes, skip |
| ocf: | Overwrite options for combined PDF/TIFF files if files with the same filename already exist in the output folder (they may have been created before the current 2PDF session). Compared to overwrite: parameter, this one works only if -pdf multipage:append or multipage:prepend is used to create multipage documents.
Example: 2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -pdf multipage:append -options ocf:createseparate |
append, createseparate, overwrite, skip |
| break_on_error: | Break on error (stop the program in case of an error) | no, yes |
| template: |
Adjust output file name template. You can enter your own file name and/or use macros:
By default, the page counter ({*SrcFileMPageNo}) appears only for multipage files split
into pages. Example: |
{*SrcFilename}{*WorksheetName}{*SrcFileMPageNo}.{*DstFileExt} |
| srcpwd: |
Input password for the source file or files (if they are password-protected). Example: -options srcpwd:123456 If a password contains spaces, input it between double quotation marks. Example: -options srcpwd:"my password" If you have files secured with more than one password, you can enter multiple passwords too (the order is not important). Example: -options srcpwd:password1 srcpwd:password2 srcpwd:password3 |
Enter password(s) for source file(s) |
| dstpwd: | Set password to create password-protect output PDF files. This way, you can protect one or multiple files at once
with a single password. Only a single password can be used within a command.
Example: -options dstpwd:123456 |
Enter password for output file(s) |
| res: |
Change rasterization resolution (DPI) of the output files. This parameter may need changing only when the OCR feature is used which results in file's rasterization. The default value is 300 which is good for most scenarios, but you can change it for your needs. The rasterization resolution can be set within the range of 72-4096. |
300 |
| attachments: | Set processing of file attachments. Attachments can be saved separately, ignored or combined with the file (append or prepend). Besides, you can convert attachments only, without the file(s). | ignore, separate, onlyatt, combine, combine_prepend |
| sort: | Sort output files. Can be sorted by different parameters like name, date, file type, and more. To sort the files in descending order, use values ending with _d (name_d, date_d, etc.). | unsorted, name, date, type, size, path, name_d, date_d, type_d, size_d, path_d |
| log: | Create events log. This parameter saves log files (in XML format) containing information about the system and records of all 2PDF events. We recommend having this parameter activated because information contained in log files will help our developers quickly identify what's happening in case of any error or issue. Example:-options log:no |
yes, no |
| logpath: | Set path to log files location for the log: parameter. By default, it is %TEMP% which usually opens the path "C:\Users\[User]\AppData\Local\Temp". Example:-options log:yes logpath:"E:\2PDF Logs" |
%TEMP% |
| reslog: | Create a resulting log file in TXT format with brief information about each session. Example:-options reslog:"C:\My folder\My_log.txt" |
|
| export_path: | Export logs and settings to a specified folder. This option exports all application logs and current settings to a specified folder as a ZIP archive. It makes it easy to quickly send all necessary information to our support team for issue diagnosis or troubleshooting. After the conversion is complete, you will see a message like: "The exported ZIP has been created in the folder: 2pdf.exe -src "C:\Files\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -options export_path:"C:\2PDF Logs" |
none |
| silent: | Suppress console output – do not show the conversion process and convert silently | no, yes |
| alerts: | Display alert windows | yes, no |
| fast_combine: | Set the number of files to quickly create a multipage PDF from them. Greatly increases file processing speed. Works with PDFs as source files only. The number of files is unlimited. Example: -options fast_combine:10000 | Enter the number of source files |
| user: | Enter username (login) for converting a web page – when URL is set as a source and if password entry is required to access the web page. Don't forget to specify both credentials – user and password. | Enter username (login) |
| password: | Enter password if password entry is required to access the web page you want to print (URL is set as a source). Don't forget to specify both credentials – user and password. | Enter password |
Example:
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -pdf multipage:split -options pages:"1,3,5-10" scansf:yes keepsf:no overwrite:yes template:"{*SrcFilename}{*SrcFileMPageNo}.{*DstFileExt}" sort:name attachments:combine dstpwd:123456 delsrc:yes silent:yes
In this example we also use -pdf multipage: split described in further section so that template:"{*SrcFilename}{*SrcFileMPageNo}.{*DstFileExt}" could take effect.
PDF format parameters for converted files (-pdf)
You can control different parameters related to the PDF format using the -pdf switch.
| Parameter | Description | Value (bold = default) |
|---|---|---|
| filever: | Select PDF version for output files | 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7 |
| pdf_a: | Convert to PDF/A. This feature works for .doc and .docx as source files. | no, yes |
| min_size: | Compress output PDF to minimize the file size. This feature works for .doc and .docx as source files. | no, yes |
| multipage: | Create a multipage PDF. Possible options:
|
asis, split, append, prepend |
| combine: | Set file name for a combined multipage file. If you want to set a filename with spaces, type it
within double quotation marks. Example: -pdf multipage:append combine:"my multipage.pdf" |
Combined.pdf |
| ocr: | Create searchable PDF using built-in OCR | no, yes |
| ocr_lang: | Select language available for text recognition via OCR. By default, it is English. Other options:
German, French, Hebrew, Japanese, Russian, Spanish, and others. You can select more than one, if your documents
are in several languages. Example: -pdf ocr_lang:English ocr_lang:German |
English German French Hebrew Japanese Russian Spanish Portuguese Polish Italian ChineseSimplified Arabic Korean Dutch |
| split_mode: | Defines how the document will be split when the multipage:split option is used. You can split a document by individual pages or by bookmark sections. |
bypages, bybookmarks |
| split_step: | Split multipage documents by page ranges. By default, multipage documents are split into single
pages. But you can change the number of pages per step, for example, to 3, which will create:
|
1 |
| bookmark: | Specifies the name(s) of bookmark sections that should be extracted. Use this parameter together with split_mode:bybookmarks. Example:-pdf multipage:split split_mode:bybookmarks bookmark:"name1" bookmark:"name2" |
none |
| keep_bookmarks: | Detect bookmarks that are present in the source files (usually Word or PDF files) and display them in the output converted files. | yes, no |
| attpath: | Adds external files as attachments to the processed documents. For example, you can attach an image, XML, or Word file to the output PDF. Example:-pdf attpath:"C:\Images\white rectangle.png" |
none |
| existing_att: | Specifies how to manage attachments that are already present in the source file.
-pdf existing_att:delete_all |
ignore, keep, delete_all |
| title: | Sets the Title value in PDF metadata. Example: -pdf title:"Monthly Report" |
none |
| subject: | Sets the Subject value in PDF metadata. Example: -pdf subject:"Project Overview" |
none |
| creator: | Sets the Creator value in PDF metadata. Example: -pdf creator:"2PDF Software" |
none |
| author: | Sets the Author value in PDF metadata. Example: -pdf author:"John Smith" |
none |
| producer: | Sets the Producer value in PDF metadata. Example: -pdf producer:"2PDF Engine" |
none |
| keyword: | Adds one or more Keywords to PDF metadata. Example: -pdf keyword:"finance" keyword:"Q1" |
none |
| creationdate: | Sets the PDF Creation Date metadata value. Use now to apply the current date or asis to leave it unchanged. Example: -pdf creationdate:now |
asis, now |
| modificationdate: | Sets the PDF Modification Date metadata value. Use now to apply the current date or asis to leave it unchanged. Example: -pdf modificationdate:asis |
asis, now |
Example:
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.docx" -dst "C:\Out" -pdf pdf_a:yes min_size:yes multipage:append combine:my-multipage.pdf ocr:yes ocr_lang:English
Operations (-oper)
You can use additional operations and options for output PDFs, such as applying a text or image watermark, page rotation, and more. Below is a list of switches and their parameters.
Page autorotation (-oper autorotate)
The program recognizes the layout of input files and can set their page orientation according to the specified parameters. Use this switch if you want to make document pages or images landscape or portrait automatically.
-oper autorotate
| Parameter | Description | Value (values in bold are set by default) |
|---|---|---|
| pages: | Select pages that need to be rotated automatically, for example "1,3,5-12"To select pages from the end of the document, use the expression "last" (last for the last page, last1 for the penultimate page, etc.). For example: 1,5,last2,last1,last | all |
| orientation: | Set page or image orientation (portrait, landscape). Once enabled, this option will apply portrait or landscape orientation to all files | portrait, landscape |
| direction: | Set auto rotation direction (clockwise or counterclockwise) | ccw, cw |
Example:
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -oper autorotate orientation:portrait direction:ccw
Page cropping (-oper crop)
This operation enables you to crop output pages. You can customize the margins (method:margins) that need to be cropped off manually for the left, right, top, and bottom side. Alternatively, you can use the autocrop method to automatically remove margins.
-oper crop
| Parameter | Description | Value (values in bold are set by default) |
|---|---|---|
| pages: | Select pages to apply cropping, for example "1,3,5-12"To select pages from the end of the document, use the expression "last" (last for the last page, last1 for the penultimate page, etc.). For example: 1,5,last2,last1,last | all |
| method: | Select method of page cropping. For margins, set the margins' size using the parameters left, top, right, and bottom. For autocrop, you may want to change color and tolerance parameters. |
margins, rect2p, rect_pwh, autocrop |
| left: | Set the left margin. Applies to margins and rect2p crop methods. | "0" |
| top: | Set the top margin. Applies to margins and rect2p crop methods. | "0" |
| right: | Set the right margin. Applies to margins and rect2p crop methods. | "0" |
| bottom: | Set the bottom margin. Applies to margins and rect2p crop methods. | "0" |
| width: | Set width of cropping rectangle for rect_pwh method. | "0" |
| height: | Set height of cropping rectangle for rect_pwh method. | "0" |
| color: | Set color sample for autocrop method. By default it is white. You can pick another color using RGBA color model –"r:(0-255),g:(0-255),b:(0-255);a:(0-255)". | "r:255,g:255,b:255,a:255" |
| tolerance: | Set tolerance value for autocrop method. Applies tolerance value for autocrop method (0-100%). Tolerance parameter specifies the allowed deviation from the color sample specified in the previous color parameter. | "0" |
| units: | Set units for setting margins or cropping rectangle size: pixels, mm, cm, inch, percents (percent of page height). | pixels, mm, cm, inch, percents |
Example:
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -oper crop method:autocrop
'Grayscale' operation (-oper grayscale)
The Grayscale operation converts documents and images to black and white during processing. This feature may be useful for reducing file size, improving readability, or preparing files for printing.
-oper grayscale
| Parameter | Description | Value (bold = default) |
|---|---|---|
| pages: | Specifies which pages to convert to grayscale. Example: "1,3,5-12" To select pages from the end of the document, use the expression "last" | all |
Example:
2PDF.exe -src "C:\Input\Document.pdf" -dst "C:\Output" -oper grayscale pages:"1,last"
Page rotation (-oper rotate)
Use this switch to rotate document pages or images.
-oper rotate
| Parameter | Description | Value (values in bold are set by default) |
|---|---|---|
| pages: | Select pages that need to be rotated automatically, for example "1,3,5-12"To select pages from the end of the document, use the expression "last" (last for the last page, last1 for the penultimate page, etc.). For example: 1,5,last2,last1,last | all |
| angle: | Set angle of rotation. Please note that you can use only right or straight angles (90, 180, 270) | 0 |
| direction: | Set direction for page rotation (clockwise or counterclockwise) | ccw, cw |
| color: | Set background color using RGB color model – "r:(0-255),g:(0-255),b:(0-255)" | r:255,g:255,b:255 |
Example:
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -oper rotate angle:90 direction:cw color:"r:0,g:128,b:0"
Resizing (-oper resize)
The Resize operation lets you change the size of output images or document pages. You can specify a new size in pixels, millimeters, centimeters, inches, or percent. Various adjustments are available.
-oper resize
| Parameter | Description | Value (bold = default) |
|---|---|---|
| pages: | Selects page range to resize (e.g. single pages, ranges, or all pages). For example, "1,3,5-12" To select pages from the end of the document, use the expression "last" | all |
| size: | Sets new image dimensions (width and height). Example: -oper resize size:"800 1200" | "0 0" |
| units: | Defines measurement units for the size parameter. Example: -oper resize units:mm | mm, pixels, cm, inch, percents |
| fmode: | Chooses how the image fits into the specified size. Example: -oper resize fmode:fill_in_size | fit_in_size, thumbnail, fit_width, fit_height, fill_in_size, none |
| falign: | Aligns the resized content within the specified size. Example: -oper resize falign:left_top | center, left_top, right_bottom |
| nozoom: | Prevents upscaling if the source image is smaller than the target size. Example: -oper resize nozoom:yes | no, yes |
| method: | Applies the rescaling algorithm. Example: -oper resize method:neighbour | bilinear, neighbour |
| color: | Sets background fill color in case the image does not fully cover the new size. Example: -oper resize color:"r:255,g:100,b:255,a:255" | "r:255,g:255,b:255,a:255" |
Example:
2PDF.exe -src "C:\Input\Document.pdf" -dst "C:\Output" -oper resize pages:"1-5" size:"800 1200" units:px fmode:fit_in_size falign:center nozoom:no method:bilinear color:"r:255,g:255,b:255,a:255"
Rasterization (-oper rasterize)
This operation optimizes file size of a PDF by rasterizing its pages into JPEG format.
-oper rasterize
| Parameter | Description | Value (values in bold are set by default) |
|---|---|---|
| pages: | Select pages that need to be rasterized, for example "1,3,5-12"To select pages from the end of the document, use the expression "last" (last for the last page, last1 for the penultimate page, etc.). For example: 1,5,last2,last1,last | all |
| res: | Change the rasterization resolution (DPI) of the output files. You can set the rasterization
resolution within the range of 72-4096. The default value is 72, which is ideal for maintaining a low file size. However, you can adjust it according to your needs. |
72 |
| quality: | Set image quality in percent. The quality can be changed within the range of 20-100. | 75 |
| antialiasing: | Use a rasterization algorithm with anti-aliasing. Anti-aliasing helps to make the edges of an image smoother, resulting in a more gradual transition and reducing the visual artifact of stair-stepped pixels. | yes |
Example:
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -oper rasterize res:150 quality:100
Text watermark (-oper textwatermark)
Use this switch to add text as a watermark. You can fully customize it by selecting the right font, size, color, angle, and positioning.
Note: When the Text watermark is applied, the pages are re-rendered, which might lead to larger file sizes and longer processing times. If you encounter this problem, consider using the Text annotation operation instead.
-oper textwatermark
| Parameter | Description | Value (values in bold are set by default) |
|---|---|---|
| pages: | Set page range for the watermark. Example: 1,3,5-12To select pages from the end of the document, use the expression "last" (last for the last page, last1 for the penultimate page, etc.). For example: 1,5,last2,last1,last |
all |
| text: | Input watermark text. Example: "Confidential" |
Type any text |
| url: | Enter a URL for the watermark. You can add a clickable web link to the text watermark | Enter URL |
| font: | Set font name, the default font is Arial. Example: Verdana |
Arial |
| fontsize: | Set font size. Example: 16 |
12 |
| fs_units: | Set font size units: points, percents (percent of image height) | points, percents |
| bold: | Make font bold | no, yes |
| italic: | Make font italic | no, yes |
| underline: | Make font underlined | no, yes |
| halign: | Set horizontal alignment | left, center, right |
| valign: | Set vertical alignment | top, center, bottom |
| offx: | Set horizontal offset value (percent of the page width) | 0 |
| offy: | Set vertical offset value (percent of the page height) | 0 |
| color: | Set text color using RGB color model – "r:(0-255),g:(0-255),b:(0-255)". Example: "r:0,g:128,b:0,a:255" |
"r:0,g:0,b:0,a:255" |
| bgcolor: | Set text background color using RGB color model – "r:(0-255),g:(0-255),b:(0-255)". Example: "r:0,g:255,b:0,a:128" |
"r:255,g:255,b:0,a:255" |
| angle: | Set angle of rotation in degrees (0-360) | 0 |
| direction: | Set direction for watermark rotation (clockwise or counterclockwise) | ccw, cw |
| border: | Draw border | no, yes |
| fit: | Fit into image | no, yes |
| method: | Set a blending method for watermark – AlphaBlend or Overdraw | alphablend, overdraw |
| zorder: | Change Z-order. You can insert the watermark behind (background) or in front (foreground) of the document's contents. | foreground, background |
| txt_margin: | Set the size of margins around text, in font units. This can be useful when you're enabling bgcolor or border parameters. | 0,0,0,0 |
Example:
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -oper textwatermark pages:"1,3-5,12" text:"(C) John Smith" font:"Verdana" fontsize:15 bold:yes italic:yes underline:yes halign:center valign:center offx:10 offy:15 color:"r:255,g:0,b:0,a:128" bgcolor:"r:0,g:255,b:0,a:128" angle:45 border:yes
Text annotation (-oper textannotation)
The Text annotation switch enables you to add text to the converted files. Unlike Text watermark, it does not re-render document pages and does not affect the document structure, thus making file processing faster.
-oper textannotation
| Parameter | Description | Value (values in bold are set by default) |
|---|---|---|
| pages: | Set page range for the text annotation. Example: 1,3,5-12To select pages from the end of the document, use the expression "last" (last for the last page, last1 for the penultimate page, etc.). For example: 1,5,last2,last1,last |
all |
| text: | Enter annotation text. Example: "Confidential" |
Type any text |
| url: | Enter a URL for the annotation. You can add a clickable web link to the text annotation | Enter URL |
| font: | Set the font name, the default font is Arial. Example: Verdana |
Arial |
| fontsize: | Set font size. Example: 16 |
12 |
| fs_units: | Set font size units: points, percents (percent of image height) | points, percents |
| bold: | Make font bold | no, yes |
| italic: | Make font italic | no, yes |
| underline: | Make font underlined | no, yes |
| halign: | Set horizontal alignment | left, center, right |
| valign: | Set vertical alignment | top, center, bottom |
| offx: | Set horizontal offset value (percent of the page width) | 0 |
| offy: | Set vertical offset value (percent of the page height) | 0 |
| color: | Set text color using RGB color model –
"r:(0-255),g:(0-255),b:(0-255)". Example:"r:0,g:128,b:0,a:255" |
"r:0,g:0,b:0,a:255" |
| bgcolor: | Set text background color using RGB color model –
"r:(0-255),g:(0-255),b:(0-255)". Example:"r:0,g:255,b:0,a:128" |
"r:255,g:255,b:0,a:255" |
| angle: | Set angle of rotation in degrees (0-360) | 0 |
| direction: | Set direction for watermark rotation (clockwise or counterclockwise) | ccw, cw |
| border: | Draw border | no, yes |
| fit: | Fit into image | no, yes |
| method: | Set blending method | alphablend, overdraw |
| zorder: | Change Z-order. You can insert the watermark behind (background) or in front (foreground) of thedocument's contents. | foreground, background |
| txt_margin: | Set the size of margins around text, in font units. This can be useful when you're enabling bgcolor or border parameters. | 0,0,0,0 |
Example:
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -oper textannotation pages:"1" text:"ID00157404" font:"Open Sans" fontsize:35 bold:yes halign:left valign:top offx:1.5 offy:1.5 color:"r:0,g:0,b:0,a:255" bgcolor:"r:200,g:200,b:200,a:255" txt_margin:"10,10,10,10"
Image watermark (-oper watermark)
Use this switch to place an image as a watermark. You can set a path to an image of a common format (PNG, JPG, BMP, GIF) and customize the watermark's parameters like size, positioning, and overlay method.
-oper watermark
| Parameter | Description | Value (values in bold are set by default) |
|---|---|---|
| pages: | Set page range for the watermark.Example: pages:"1,3,5-12"To select pages from the end of the document, use the expression "last" (last for the last page, last1 for the penultimate page, etc.). For example: 1,5,last2,last1,last | all |
| image: | Set path to watermark image. Example: image:"C:\Watermark.png" | |
| url: | Enter a URL for the watermark. You can add a clickable web link to the text watermark | Enter URL |
| halign: | Set horizontal alignment | left, center, right |
| valign: | Set vertical alignment | top, center, bottom |
| offx: | Set horizontal offset value (points) | 0 |
| offy: | Set vertical offset value (points) | 0 |
| size: | Set watermark size as a percent of page width and height. It is possible to set original image size (as is) | -1, as is |
| angle: | Set angle of rotation, by default it is 0° | 0 |
| direction: | Set direction of rotation: clockwise or counterclockwise | ccw, cw |
| method: | Set a blending method for watermark – AlphaBlend or Overdraw | alphablend, overdraw |
| zorder: | Change z-order. You can insert the watermark behind (background) or in front (foreground) of the document's contents. | foreground, background |
Example:
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -oper watermark pages:"1,3-5" image:"C:\my logo.png" halign:right valign:top offx:10 offy:15
Draw rectangle (-oper paint)
Use the -paint switch to draw a rectangular border around the content of the output pages.
-oper paint
| Parameter | Description | Value (values in bold are set by default) |
|---|---|---|
| pages: | Set page range for this operation.Example: pages:"1,3,5-12"To select pages from the end of the document, use the expression "last" (last for the last page, last1 for the penultimate page, etc.). For example: 1,5,last2,last1,last | all |
| cmd: | Select rectangle application: fill or draw | fillrect, drawrect |
| rect: | Set rectangle dimensions in the format: "x0 y0 width height" | "0 0 -1 -1" |
| pen_color: | Set draw color in the format: "r:(0-255),g:(0-255),b:(0-255),a:(0-255)" | "r:0,g:0,b:0,a:255" |
| brush_color: | Set fill color in the format:"r:(0-255),g:(0-255),b:(0-255),a:(0-255)" | "r:255,g:255,b:255,a:255" |
| pen_width: | Set thickness of rectangle's frame | 1 |
| units: | Set draw units: pixels or percents | pixels, percents |
| zorder: | Change z-order. You can insert the rectangle in the background or in the foreground of the document's contents. | foreground, background |
Remove blank pages (-oper removeblankpages)
This switch allows you to automatically remove unnecessary blank pages during processing.
-removeblankpages
| Parameter | Description | Value (values in bold are set by default) |
|---|---|---|
| pages | Set page range for this operation. Example, "1,3,5-12"To select pages from the end of the document, use the expression "last" (last for the last page, last1 for the penultimate page, etc.). For example: 1,5,last2,last1,last |
all |
| pt | Set pixel threshold (0-100%). | 0.5 |
| ct | Set channel threshold (0-100%). | 4 |
Post-processing actions (-postproc)
Use the -postproc switch to сopy, move, or delete files automatically after processing, if necessary.
-postproc
| Parameter | Description | Value (values in bold are set by default) |
|---|---|---|
| passed: | Select action for successfully converted files: copy, move, or delete | none, copy, move, delete |
| passed_dir: | Specify a folder where successfully convert files should be moved or copied to. For
example: -postproc passed:copy passed_dir:"C:\Converted" |
Enter path to folder |
| passed_delsf: | Delete empty unused subfolders from the source folder | no, yes |
| failed: | Select action to be performed with files that were not converted: do nothing, copy/move to another folder, or delete | none, copy, move, delete |
| failed_dir: | Select action for files that failed to convert. For example:-postproc failed:move failed_dir:"C:\Failed" | Enter path to folder |
| failed_delsf: | Delete empty subfolders after failed files were moved or deleted from there. | no, yes |
| keepsf: | Keep the same subfolder structure as in the input folder (if a folder is set as a source). | no, yes |
| output: | Select action for output files: keep all, delete failed, or delete all if at least one failed | keep, delete, delete_all |
File loading settings (-fls)
The -fls switch contains parameters that control what settings 2PDF applies to the input files before the conversion.
-fls excel
| Parameter | Description | Value (values in bold are set by default) |
|---|---|---|
| esm: | Set export scale mode for Excel files. | original, fit |
-fls imageraster
| Parameter | Description | Value (values in bold are set by default) |
|---|---|---|
| iccprofile: | Select action if a source file contains a color profile | ignore, embedded, embedded_non_rgb |
| iccpath: | Set ICC profile file path. For example:"C:\My folder\CMYK.icc" |
Load custom 2PDF Settings file (-inipath)
The -inipath switch enables you to load previously saved custom 2PDF Settings. These settings are saved using the Export button as a "2PDF-settings <date>.ini" file. By including the path to this settings file, you can apply specific default settings to your 2PDF command if needed.
Example:
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -inipath "C:\In\2PDF-settings 2023-12-25.ini"
Information (-info)
pagecount:
Get the number of pages of a file as executable's exit code. This command generates a code with the number of pages contained in a single file as executable's exit code. For example, Page count=5.
Example:
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\Text.pdf" -info pagecount
bookmarks:
Get the document's list of bookmarks as return code. This command generates a code with a list of bookmark names.
Example:
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\Text.pdf" -info bookmarks
Command lines (-cmdlines)
The -cmdlines switch allows you to set the path to a TXT file that contains the command (or multiple commands) that need to be executed. This can be helpful when the command is very long or if you want to run several commands sequentially.
2PDF.exe -cmdlines "C:\Folder\commands.txt"
Default settings (-ini)
The default settings are available in the editor with GUI controls. To access it, use this command:
2PDF.exe -ini
The Default Settings define the settings values for each 2PDF session (unless other values are specified in the command line which will override them). So you can set up everything only once, and they will be applied every time you use 2PDF. If you are not sure about a specific setting, please contact our support for assistance.
Examples
Convert to PDF all files from folder "C:\In" with all subfolders
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out"
Combine all files from folder "C:\In" to a single multipage PDF file
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -pdf multipage:append combine:"my multipage.pdf"
Convert all files from folder "C:\In" to searchable PDF
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -pdf ocr:yes ocr_lang:English
Convert to PDF all files, listed in a text file "C:\tests\list.txt"
2PDF.exe -src "@C:\tests\list.txt" -dst "C:\Out"
Quickly combine a large number of PDFs (10000 files) from folder "C:\In" and save the output file as "C:\Out\output.pdf"
2pdf.exe -src "C:\in\*.pdf" -dst "C:\Out" -pdf multipage:append combine:"output.pdf" -options fast_combine:10000
Split multipage files into separate PDF pages
2pdf.exe -src "C:\in\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -pdf multipage:split
Password-protect multiple documents (batch lock files)
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -options dstpwd:password
password – enter a password which will be applied to all source files
Remove password from multiple secured documents (batch unlock files)
2PDF.exe -src "C:\In\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -options srcpwd:password1 srcpwd:password2 srcpwd:password3
password1, password2, password3 – if, e.g., files within a folder have 3 different passwords
Combine emails with attachment(s) to PDFs and keep the original file name
2PDF.exe -src "C:\Emails\*.*" -dst "C:\Out" -pdf multipage:append combine:{containername}.pdf
